The QNT Editor
![]() The General Tab Page
The General Tab Page
The General tab page contains global settings for the following worksheets: ![]() Peak Table ("Retention Time Settings"), Amount Table ("Amount Interpretation"), and
Peak Table ("Retention Time Settings"), Amount Table ("Amount Interpretation"), and ![]() Calibration ("Global Calibration Settings"). Enter a name for the current QNT File in the Title field. The name appears in the Browser and can be included in a Report when printing data of the QNT Editor. Click Unidentified Peaks to determine how Chromeleon quantifies unidentified peaks.
Calibration ("Global Calibration Settings"). Enter a name for the current QNT File in the Title field. The name appears in the Browser and can be included in a Report when printing data of the QNT Editor. Click Unidentified Peaks to determine how Chromeleon quantifies unidentified peaks.
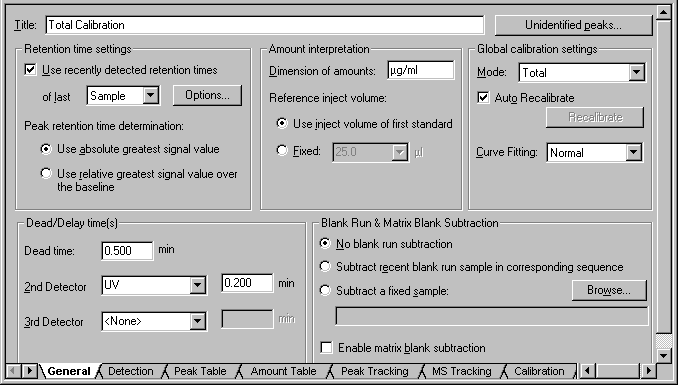
Retention Time Settings
Select the Use Recently Detected Ret. Times check box to use the Retention Time of the preceding sample to identify a peak via a retention time window (Window). You can also use the retention time of the last standard. Select Standard from the of last drop-down list. Click Options… to display more options. (For more information, refer to Use Recently Detected Retention Time.) This function allows the system to automatically react to changing retention times that are, for example, due to column trends. If the option is disabled, the actually determined retention time listed in the peak table is used for identifying the peak.
In the Peak retention time determination section, specify how the retention time of peaks are determined: Select Use absolute greatest signal value to use the retention time of the greatest absolute signal value. Select Use relative greatest signal value over the baseline to use the retention time of the greatest relative signal value, i.e., of the largest distance to the baseline.
Dead/Delay time(s)
Enter the Dead Time in the Dead Time field. The dead time is used for calculating the Capacity Factor k' and the Kovats Indexes.
Select the name of any further detector from the 2nd Detector and/or 3rd Detector drop-down list and enter the Delay Time in the min field. (Also, refer to Integrating Chromatograms and Identifying Peaks ![]() Defining the QNT Method for Several Detectors.)
Defining the QNT Method for Several Detectors.)
Amount Interpretation
For documentation purposes (exclusively), the physical dimension (amount or concentration) that is used for the amount values can be included in the field Dimension of Amounts. Amount values are not automatically converted into concentration values or vice versa.
In addition, the reference injection volume is defined on this page. Either select the injection volume of the first standard (Use inject volume of first standard) or enter any volume via Fixed.
Global Calibration Settings
Use the Mode field to determine how the samples of a sequence are calibrated and on which Calibration Mode the calibration is based. For example, this allows you to calibrate certain samples as a group or to include calibration samples for samples that are analyzed later. For more information, refer to Integrating Chromatograms and Identifying Peaks ![]() Calibrating.
Calibrating.
When Auto Recalibrate is enabled, each modification within a chromatogram such as moving peak delimiters results in automatic recalculation of the Calibration Coefficient and all derived calibration data. Disable Auto Recalibrate in the peak table to include the c0, c1, c2, and/or c3 columns. Perform recalibration by clicking Recalibrate. You may enter the corresponding values manually, as well.
Curve Fitting allows you to determine dependent and independent variables for calibration: Select Normal to accept normal evaluation and the axis settings of the calibration curve (x-axis = amount, y-axis = measured value). Select Inverted to use inverted evaluation and to invert the axes (x-axis = measured value, y-axis = amount). For more information, refer to Calibrating ![]() Inverting Dependent and Independent Variables.
Inverting Dependent and Independent Variables.
Blank Run & Matrix Blank Subtraction
In the Blank Run & Matrix Blank Subtraction section, determine whether the absorption values of a Blank Run Sample are considered (= subtracted) in the sample evaluation (= Blank Run Subtraction). You can also subtract the results of a single Matrix Blank Sample.
Select No Blank Run Subtraction if no correction is to be performed.
Select Subtract Recent Blank Run Sample in Corresponding Sequence to use a finished blank run sample of the current sequence for the subtraction. Chromeleon subtracts the chromatogram of the blank run sample from the active chromatogram, point by point.
Select Subtract a Fixed Sample to perform the correction with any sample. Click Browse to search for the sample.
Select Enable Matrix Blank Subtraction to enable the subtraction of matrix blank samples. Contrary to the other options, the resulting peak areas or peak heights are subtracted.
Also, refer to Integrating Chromatograms and Identifying Peaks ![]() Subtracting a Blank Run Sample.
Subtracting a Blank Run Sample.