Location:
Peak Table tab page
Report Variable (Peak Table)
Related Variables:
Description:
Data exchange between laboratories for substance identification based on relative retention times is not exact. Therefore, especially in gas chromatography, retention indexes are used. They use a series of chemically similar standard substances to achieve uniform scaling of the Retention Time.
Advantage is taken of the fact that within a homologous series of compounds the logarithms of the adjusted retention times are proportional to the number of carbon atoms (adiabatic and isothermal conditions presumed). The most frequently used Kovats Index is defined as follows:
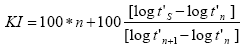
Where:
KI = Kovats index
t'S = Adjusted retention time (with tS = t'S + t0)
tS = Retention time
t0 = Dead time
n = Number of carbon atoms (normally of n-alcane)
S = Substance of interest
The following must be true:
![]()
In Chromeleon, the Kovats Index is defined for certain master peaks on the Peak Table tab page of the QNT Editor. For more information, refer to How to …: ![]() Defining the Retention Index and the Kovats Index.
Defining the Retention Index and the Kovats Index.
On the basis of the defined values, Chromeleon calculates the Kovats index for the remaining peaks. Use the Kovats Index variable to display the results in the report.
The following formula is used for the calculation:
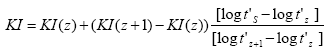
With KI = Kovats index (usually KI = 100 * n is entered) and
z = number of the marker peak.
If no marker peaks or no dead time is determined, the Kovats index is not defined (n.a.). In addition, the Kovats index is not defined for any peaks that occur before the first and behind the last marker peaks.
![]() Note:
Note:
In Chromeleon, the substances of interest must be between two marker peaks.