Access Control
The Chromeleon network capabilities allow you to perform any operation from any workstation (Client). Similar to the network itself, Chromeleon provides a comprehensive system for user management. The User Manager and the Security Activation Tool (CmUser and CmSecure programs) allow the system administrator to control access to data, systems, and workstations.
This is to ensure that only authorized users can access specific Timebases, data, Datasources, directories, Sequences, templates, etc.
![]() Tip:
Tip:
For more information about these two programs, refer to ![]() Chromeleon User Management. For a brief summary, see below.
Chromeleon User Management. For a brief summary, see below.
Access-protected operations include:
Creation, modification, and deletion of datasources, directories, sequences, samples, work lists, workspaces, Queries, server configurations, timebases, spectra libraries, Control Panel, report definitions, and quantification methods (QNT Files).
Start of data acquisition, Batch processing and export and printing of batch data.
Electronic Signature of sequences.
Saving and deletion of peak manipulations.
Backup and restoration of datasources, directories, and sequences.
Data import and export.
Access to Servers and timebases.
Granting Privileges
The Chromeleon administrator grants the privileges, defining the scope of functions available to each user when access control is enabled. In addition, the system administrator assigns the corresponding passwords.
When access control is enabled for a workstation to which a user logs on with the appropriate Password, his(her) "personal" privileges are available on this workstation. It is not important on which workstation the user logs onto the system.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
Clients that are not subject to access control can access any unprotected objects of other clients on the network. A datasource can be accessed on the network when the datasource directory is shared in the Windows Explorer. Access can be restricted by assigning an Access Group in the Chromeleon Browser. Select the datasource, and then select Properties on the context or File menu. On the Access Control tab page, use the Add and Remove buttons to determine which Access Groups shall be authorized to access the object.
In the Server Configuration program, select Properties, and then restrict the operations that can be performed from another PC. For example, deselect the Control check box in the Allow Remote section. This allows users from other PCs to monitor the timebase but not to control it (see example below).
Executing Privileges
In general, personal access options and Privileges are already defined when the Chromeleon user logs onto the system. Thus, the user can perform all tasks available on the screen or accessible via mouse click, but (s)he has no influence on the status of the entire system.
This may be different for users who are granted extensive privileges. These users are allowed to change access to datasources, directories, sequences, servers, and timebases. When they select the object in the Browser or in the Server Configuration program, and then select Properties on the context menu, they can change the access group assignment as desired. In addition, they can also lock datasources, directories, and sequences. A red lock (![]() ) on an icon indicates that the object is locked.
) on an icon indicates that the object is locked.
User Manager and Security Activation Tool
Chromeleon provides two separate programs for the Chromeleon administrator, the User Manager (CmUser program) and the Security Activation Tool (CmSecure program), to enable User Mode. The setup for both programs is located in the CmUser directory on the Chromeleon software CD. Please note that they are not automatically copied to the program directory.
The User Manager is protected by a password. Thus, only the administrator or persons with similar authority can open this program.
![]() Tip:
Tip:
Dionex recommends installing the Chromeleon User Management applications (CmUser directory) to a suitable network location, CD-ROM, or a USB stick to allow modifications via the network. Make sure that only Chromeleon administrators with administrator privileges for the CmUser database can access this network location.
The User Manager (CmUser program) allows you to manage the Users, Privileges, and Access Groups. The Chromeleon administrator can perform the following actions:
Create and edit Access Groups
Create and edit Privilege Groups (or P Groups)
Create and edit users in Chromeleon. The system administrator can define the userís name and job title, the Logon and signature Passwords, and the behavior if the logon failed.
The Security Activation Tool (CmSecure program) allows enabling and disabling User Mode on the Chromeleon clients and selecting the CmUser database. The user database contains the status and the rights of each user. When User Mode is enabled, the user has to enter a password to start Chromeleon. It is only possible to sign sequences electronically when the User Mode is enabled (see Electronic Signature).
A user can access an object if (s)he belongs to an Access Group granting access to this object. The operations the user is allowed to perform are determined by the his(her) privileges, which depend on the Privilege Group membership.
Example
Two timebases, TB1 and TB2, are established in Chromeleon. They can be operated by five users, U1, U21, U22, U31, and U32. U1 is the Chromeleon administrator who has unlimited access to all Chromeleon objects. U21 and U22 are users authorized to record data in both timebases; U31 and U32 are users who are only authorized to perform analyses on TB1. The Chromeleon administrator needs to set up the users and Access Groups in the User Manager program as follows:
Users: U1, U21, U22, U31, and U32,
Access Groups: A1 (member: U1), A2 (members: U1, U21, and U22) and A3 (members: U1, U31, and U32),
After having created these groups, the Chromeleon administrator assigns the access groups for the two timebases, TB1 and TB2 by selecting the corresponding timebase in the Server Configuration program and Properties on the context or Edit menu.
For example, the timebase configuration for TB2 has to be as follows:
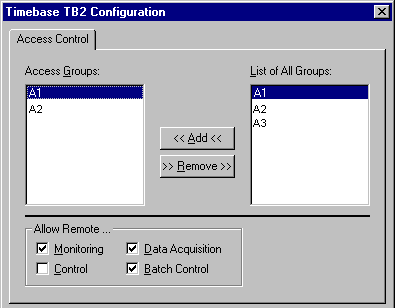
Only the users who belong to the groups A1 and A2 are authorized to access the timebase TB2.
In contrast, timebase configuration for TB1 has to comprise all three access groups:
For more information on assigning access groups on server and timebases, refer to: