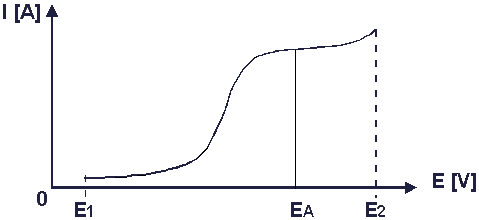
SCAN Mode
The SCAN Mode of an electrochemical detector serves to determine the analytical potential of a substance.
At a constant concentration in the flow cell that is, for example, realized by strongly reducing or by stopping the pump flow, the potential between reference and working electrode is changed linearly.
The change is either a linear increase or decrease between two values (E1 and E2; Half scan), or an increase with a subsequent decrease (Full scan). If the increase and decrease are constantly repeated, this is referred to as Continuous scan.

In all three cases, current/voltage curves (here represented by a half scan) are recorded. The working electrode potential (= EA) here corresponds to the optimum analytical potential of a substance. You have to define this potential to ensure accurate analysis in DC Mode and PULSE Mode.
Practical Application with the Antec Detector DECADE
The analysis is performed in the DC mode or the PULSE mode. If the peak of a substance is detected for which the analytical potential is to be determined, stop the pump flow, switch to the SCAN mode, and slowly change the potential. When the final value is reached, return to the previous mode and reset the pump flow to its original value.
The entire process can be performed by a key click if the required commands are available on a script button.
On the signal plot of the Control Panel, the following curve can be observed.
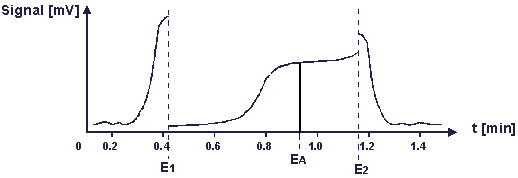
Unlike the pump, the chromatogram run time is not stopped. The retention times of the subsequent peaks will be shifted accordingly. However, the signal height of the peaks will be lower as part of the substance is "used up" during the Scan mode.
The optimum analytical potential cannot be directly read on the y-axis (time axis), but is determined with the printed chromatogram.