Mass Spectrometer
Mass spectrometers were developed to analyze the structure of unknown, mostly organic compounds. When mass spectrometers are used together with chromatographic separation procedures, they allow the qualitative and quantitative analysis of complex mixtures of substances.
Mass spectrometry includes four steps:
Sample loading (neutral molecules)
Ionization of individual molecules
Ion separation according to their masses
Ion registration in form of a Mass Spectrum
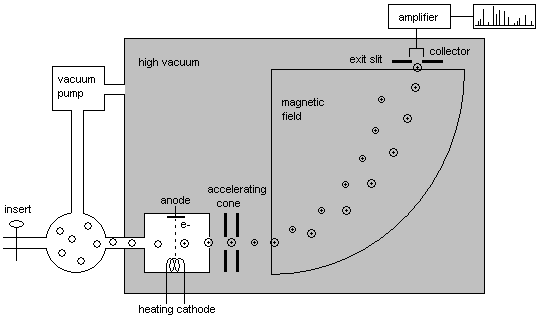
Different processes can be used for ionizing and separating ions with different masses. The following image illustrates ionization by means of an electron impact and the subsequent mass separation by means of a vertical magnetic field:

The ions that are created via the electron impact are first accelerated by means of the cones and then separated according to their mass in the magnetic field. Due to the varying intensity of the magnetic field (or the accelerating voltage), ions of different masses are directed through the exit slit into the collector and registered. In this way, mass spectrometers perform a mass scan similar to the wavelength scanning of many photodiode array detectors.
For information about how to record and process MS Data in Chromeleon, refer to ![]() Using Mass Spectrometers.
Using Mass Spectrometers.