Calibration Examples
![]() Calibration Mode: Additional
Calibration Mode: Additional
The following example illustrates the difference between the Total and Additional Calibration Modes.
Independently from the standard method, this mode determines which standard samples are used for evaluating a specific unknown sample. The position of the unknown sample in the sample list is decisive here.
Extending the Example: External Calibration/Mode: Total
Two standard samples are injected after two unknown autosampler have been injected. This results in an alternating list of two standard samples: two unknown samples, two standard samples, etc. All other settings are maintained; that is, two-point calibration is performed. The calibration is verified by additional replicates.
a) User Input:
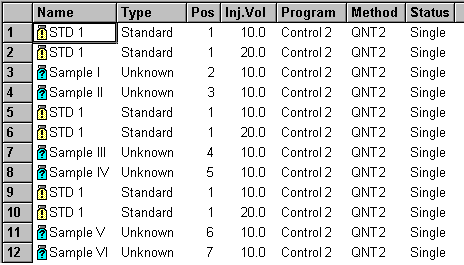
Sample List
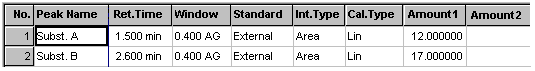
QNT Method/Peak Table Tab
QNT Method/General Tab
If the user selects the Additional mode, each unknown sample is evaluated based on the standard samples analyzed so far.
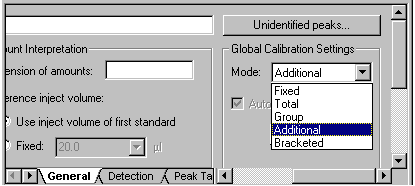
This means:
As before, samples I and II are evaluated by means of a two-point calibration. However, four analyzed standard samples are available for the samples III and IV. The result is a two-point calibration with two replicates each. Finally, the samples V and VI are evaluated by means of a two-point calibration with three replicates each.
QNT Method/Calibration Tab
The page shows all standard samples (of one sequence) that can be used for calibrating the current sample.
Press the F4 key or the SHIFT+F4 key combination to open the samples one after the other. The standard samples forming the basis for calibration are shown for each sample.
Thus, two standard samples are displayed for the samples I and II, four standard samples are displayed for the samples III and IV, and six standard samples are displayed for the samples V and VI (see below).
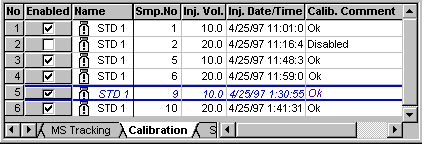
If you notice that an error occurred during the analysis of the standard sample, you can "exclude" this standard. Remove the standard in the Enable column on the Calibration tab page of the QNT Editor. Only the standard samples labeled X are considered for the calibration.
b) Evaluation:
Evaluation is similar to the example with external calibration (mode: Total). The only difference is:
The calibration curve is created for the different samples based on a different number of replicates.
This can affect the calculated calibration coefficients and thus the result, but does not necessarily do so. Normally this type of calibration is used to adapt to changed column conditions. Thus, it may happen that after a several samples, a specific substance cannot elute 100 percent from the column. As this will also be the case with the standard substance, the result is corrected automatically.
For an overview of the different calibration
possibilities provided by Chromeleon, refer to How
to …: ![]() Calibrating.
Calibrating.