Theory of Calibration
![]() Calculating the Calibration Curve
Calculating the Calibration Curve
Calculation of the calibration curve (Calibration Function) is based on the method of least squares. With a given calibration type (linear, linear with offset, etc.), the parameters of the calibration curve F(a), i.e., c0, c1, c2, and c3, are determined so that the sum of the squared distances of all measured points becomes negligible. For this purpose, the following optimization problem is solved:
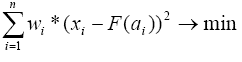
(xi- F(ai)) refers to the distance of the xi-value from the calibration curve F(a), wi is the selected weighting (see Weights, for example, wi=1, wi=1/Amount or wi=1/Amount2) and xi is the actual value.
The formula used for calculating the calibration curve depends on the ![]() Standard Method (External/Internal/…). For information about these formulas, refer to
Standard Method (External/Internal/…). For information about these formulas, refer to ![]() Evaluation with Various Standard Methods.
Evaluation with Various Standard Methods.