Cyclic Voltammetry
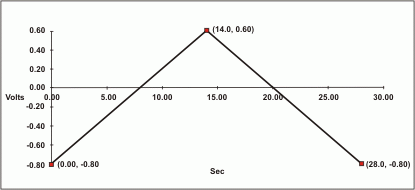
Waveforms for integrated amperometry are usually developed using information gathered with an electrochemical technique called cyclic voltammetry, in which the current that results from oxidation or reduction reactions is measured against the voltage applied to the system. The applied voltage is changed (scanned) within preset limits.
In cyclic voltammetry, the voltage is first scanned in one direction and then the scan direction is reversed so that the voltage at the end of the scan is the same as at the beginning. This results in a triangular Waveform as shown in the example below.
