Defining System Suitability Tests
![]() SST Example: Amount Deviation on Reinjection
SST Example: Amount Deviation on Reinjection
For reinjections from the same vial, the relative standard deviation of the determined Amount values should be as small as possible. To check whether the standard deviation is below a specified minimum value, follow the steps below.
If no System Suitability Test has been created yet, double-click the empty line on the SST tab page to open the SST Wizard. If a System Suitability Test already exists, select the bottom line of the test and press the DOWN ARROW key to open the wizard. The wizard guides you through test creation. Clicking Next> takes you to the next wizard page.
On the Sample Condition page, specify for which samples the test is performed. The default setting is Apply on all Samples.
On the Test Condition page, enter an appropriate name for the new System Suitability Test, e.g., Amount Deviation.
Determine the Test Condition, e.g., peak.amount >= 1. (In this case, 1 is the maximum allowed deviation expressed as a percentage.)
Click the "…" button to the right of the Test Condition input field.
In the dialog box, select Peak Results from the Categories list, and then select Amount from the Variables list.
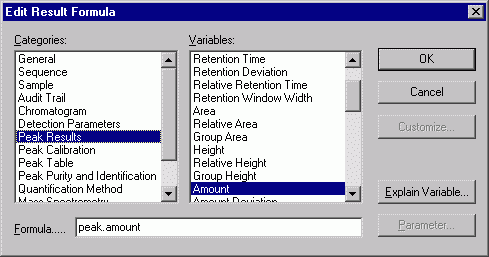
Click OK to confirm your selection and return to the SST Wizard.
In the Operator input field, select >=. In the Value input field, enter 1.
Select the Use aggregation check box. Clicking Next> takes you to the Aggregate page.
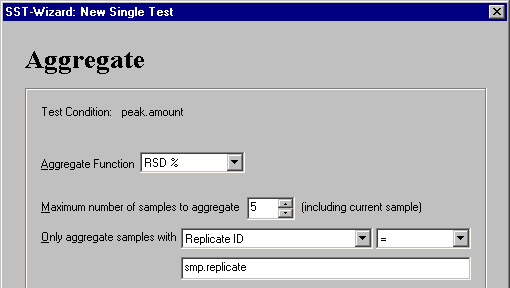
On the Aggregate page, select RSD% from the Aggregate Function drop-down list.
Enter the Maximum number of samples to aggregate, e.g., 5.
For Only aggregate samples with, determine Replicate ID = smp.replicate. This searches for a maximum of four previous samples for which the replicate ID matches the replicate ID of the current sample. The relative standard deviation of the Amount value is determined for a maximum of five samples--for the current sample and up to four others.
Use the next wizard page to determine the peak(s) and the channel for which the test is performed.
Finally, determine the test result if the test cannot be performed and what action is taken if the test fails.